Authentication
Overview
Glean's authentication system supports the OAuth 2.0 standard for securing action requests. This guide covers the available authentication types and how to verify requests from Glean.
Authentication Types
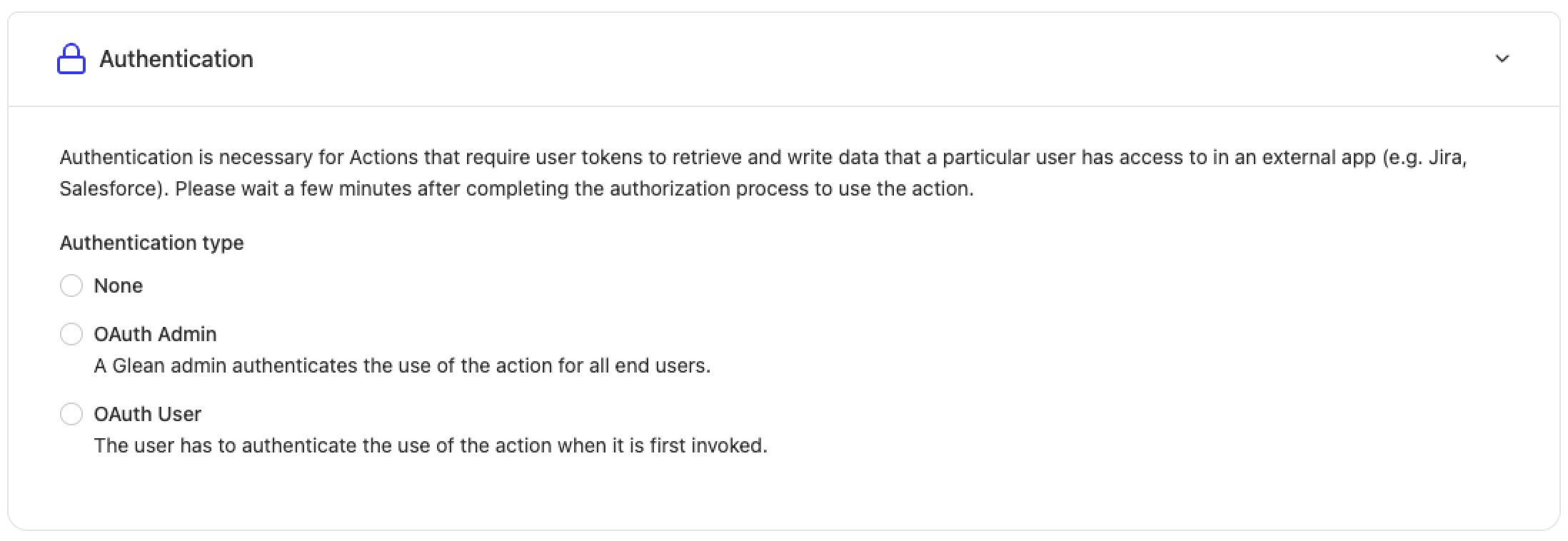
OAuth Admin
Requires one-time authorization by the action developer or app admin during setup. After authorization, Glean sends the token for all requests from authorized users.
OAuth User
Requires initial OAuth connection setup by the developer/admin. Users must authorize the action on first use, after which their token is used for subsequent requests.
None
No tokens are provided in the request. Choose this if you don't require specific tokens from Glean to handle requests.
When using "None" authentication type, it's highly recommended to implement request verification to ensure requests are coming from Glean. Without additional protections (e.g., VPN, Firewall), your endpoint would be publicly accessible.
OAuth Configuration
When setting up OAuth (admin or user), you'll need to configure the following parameters using the OAuth authorization_code grant type:
| Parameter | Type | Required | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Client ID | string | ✓ | The client ID for your OAuth application |
| Client Secret | string | ✓ | The client secret for your OAuth application |
| Client URL | string | ✓ | The URL used to redirect users for authentication |
| Authorization URL | string | ✓ | The URL Glean uses to complete OAuth by issuing a POST request with the authorization code |
| Scopes | string | Optional parameter for relevant application scopes. Consider adding offline_access scope if supported to ensure refresh tokens are sent (reference) |
Your OAuth App must be configured to allow redirects (Callback URL) to:
https://<your-server-url>/tools/oauth/verify_code
Find your server URL at app.glean.com/admin/about-glean.
Without this, the OAuth integration may fail or show invalid redirect URI errors.
Request Verification
While optional, implementing request verification is highly recommended to enhance the security of your action server endpoints.
Glean provides a JWT-based signature in the Glean-Actions-Signature header, signed using RSA-SHA256. The signature can be verified using your Glean instance's public key.
JWT Claims
The JWT header includes these standard claims:
iat- Issued at timeexp- Expiration timeiss- Issuer (always set to 'glean')
Implementation Examples
- Python
- Java
import jwt
import json
import requests
# Fill your glean instance here.
YOUR_GLEAN_SERVER_URL=''
# Find your server URL at app.glean.com/admin/about-glean
# Use this function as is in your code (once you have filled out YOUR_GLEAN_SERVER_URL).
# Pass the header value for Glean-Actions-Signature as the 'token' in this function.
def verify_jwt(token):
try:
# First, we fetch the public key JSON response.
response = requests.get(f"{YOUR_GLEAN_SERVER_URL}/api/tools/v1/verification_key")
response.raise_for_status() # Raises an exception for 4XX/5XX responses
public_key_str = response.json()['publicKey']
# Second, we convert this into the PEM format.
pem_key = f"-----BEGIN PUBLIC KEY-----\n{public_key_str}\n-----END PUBLIC KEY-----"
# Finally, we attempt to decode the token using the public key.
decoded = jwt.decode(token, pem_key, algorithms=['RS256'], issuer='glean')
return True
except jwt.PyJWTError as e:
# Handle error (e.g., token expired, token tampered, etc.)
print(f"JWT verification failed: {e}")
return False
import java.util.Base64;
import java.security.KeyFactory;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.security.PublicKey;
import java.security.spec.InvalidKeySpecException;
import java.security.spec.X509EncodedKeySpec;
import org.jose4j.jwa.AlgorithmConstraints;
import org.jose4j.jwt.consumer.InvalidJwtException;
import org.jose4j.jwt.consumer.JwtConsumer;
import org.jose4j.jwt.consumer.JwtConsumerBuilder;
public static void verifySignature(String publicKey, String jwtFromHeader) throws IOException {
byte[] derKey = Base64.getDecoder().decode(publicKey);
final X509EncodedKeySpec keySpec = new X509EncodedKeySpec(derKey);
PublicKey rsaOrEcKey;
try {
rsaOrEcKey = KeyFactory.getInstance(JWT_ALG).generatePublic(keySpec);
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException e) {
// This should never happen, since we're using a standard algorithm.
throw new RuntimeException(e.getMessage());
} catch (InvalidKeySpecException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Unhandled exception during public key setup: " + e.getMessage());
}
AlgorithmConstraints constraints =
new AlgorithmConstraints(AlgorithmConstraints.ConstraintType.WHITELIST, "RS256");
JwtConsumer jwtConsumer =
new JwtConsumerBuilder()
.setRequireExpirationTime()
.setRequireIssuedAt()
.setAllowedClockSkewInSeconds(30)
.setExpectedIssuer("glean")
.setVerificationKey(rsaOrEcKey)
.setJwsAlgorithmConstraints(constraints)
.build();
try {
jwtConsumer.processToClaims(jwtFromHeader);
} catch (InvalidJwtException e) {
throw new IOException("Failed to verify actions signature: " + e.getMessage());
}
}